
Due to development in science technology, marine development is now easier and the infinite potential of the sea has unveiled. As a result, there is a greater interest in the seas than ever before. Each country is arguing for the extension of EEZs and continental shelves, but as there are overlaps in the waters under contention, there is a fierce dispute to gain even a bit more of the marine territory.
Moving beyond national waters, there is also a heated competition to occupy marine territories such as polar areas and the deep sea that are yet without an owner. In particular, the UK, Chile, and Argentina are some of the countries in conflict over the South Pole, and more and more countries are lining up to join the fight. In such a global trend, there is also a need for Korea to put greater efforts into guarding national waters and go beyond to acquire new marine territories.
In the past, marine resources were often used to refer to sea resources, but now, with improvements in marine development technology and increase in the use of the sea, it has come to apply to all of sea resources that are available for use.
More recently, the marine space itself has been included as a type of resource, as the so-called “fourth marine resource.” This can be explained by the fact that land space for residence and commercial use are decreasing.
Marine resources can be divided into four categories: marine mineral resources, marine energy resources, marine life resources, and marine space
For countries like Korea that have high dependence on trade, the sea is extremely important as a traffic route. Today, many countries are seeing an increase in dependence on maritime trade due to economic growth, rising foreign trade and heightening amount of crude oil imports. Maritime trade serves as a link between economic mutual reciprocity from country to country and region to region. In addition, in terms of global trade, it creates significant economic profits as a leading instrument for trade.
Since Korea is positioned on the main course of advancing from continent to ocean, it is equipped geographically to sail to any place on Earth via the sea route. Furthermore, it is the hub of marine transportation located on the sea route between Southeast Asia and North America. Against this background, the Busan Port is a rising global hub of logistics with its customized service using world’s best facilities and technologies. This fact well displays the importance of maritime trade and sea route in Korea’s economic activities.

Busan Port: Korea’s number one port that is always busy with imported and exported goods and numerous ships that travel from one part of the world to another. As of December 2013, it was ranked fifth in the world in management of container goods.
The melting of icebergs in the Arctic Ocean due to global warming has emerged as an environmental problem. But at the same time, with the opening of the North Pole route, maritime trade has its eyes on a new opportunity. In July 2009, two German commercial ships successfully sailed from Asia to Europe via the North Pole route. It was a historical moment of opening the Arctic Ocean as a new trade route, which was previously impossible to use due to thick icebergs.
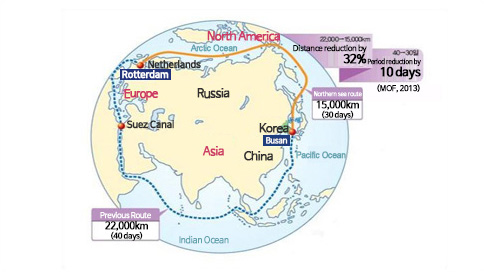
The reason behind the attention on the North Pole route is the significant reduction in distribution costs. In a usual journey from Busan to Rotterdam, Netherlands, the use of North Pole route could reduce the distance by about 7,000 km and period by 10 days from the previous Indian Ocean route that passes through the Suez Canal. By 2020, maritime shipping through the North Pole route is expected to increase over eight fold. It is an opportunity for economic growth as well as exploration of new territorial waters.
The term sea route, which refers to the seaway, is used comprehensively to mean a strategic network and facilities for uninterrupted transportation of people and goods at seas. However, it was originally used in military strategies to mean sea pathways linking troops and bases for transporting supplies and augmentation forces. In other words, it was recognized as an important space in light of military strategies.
Seas surrounding land play a critical role in maintaining national security. From the past to today, most hegemonic countries stretched out to the wider world while maintaining national security based on powerful maritime power.
Marine transportation accounts for the absolute majority of shipping in trade between countries. Therefore, it has become an interest of many countries to ensure safety on sea routes to secure stable maritime transportation.
The damage from piracy or marine terrorism is not limited to the victimized ship but could threaten the safety of the transportation route in whole. In the Malacca Straits, where some 50,000 commercial ships pass through annually, pirates appear frequently. Korea transports 99% of crude oil imports, 83% of coal and gas, and 35% of imported and exported goods through Malacca Straits. Therefore, if it gets blocked as a result of piracy or marine terrorism, it could become a national issue. This is true for many other countries also using Malacca Straits.
While there are direct damages from piracy, the secondary damage following the attack is also significant. Insurance costs increase and distribution costs will also hike up. These will have an effect on the economy overall. According to a research, if a sea route gets blocked for 15 days, Korea’s basic industry, then manufacturing and constructions industries will become paralyzed and lead to constraints in daily life and public transportation. Therefore, ensuring safety of sea routes on international trade routes is a requirement of safeguarding seas. As great an effect it can have on people’s lives and the global economy, a thorough preparation is needed.
Marine space has always been closely related to human lives. Coastal regions have been an important residential area since the past. Today, about 50 % of the world population lives within 50km from the coastline to inland.
Recently, marine space is changing from a mere residential space to that for new marine development and construction. The Incheon International Airport in Korea, the Kansai International Airport in Osaka, Japan, and Palm Jumeirah in United Arab Emirates are examples of models maximizing marine space with landfill or artificial islands.
Meanwhile, following the revitalization of leisure and the tourism industry, marine space is ready to undertake another change. Diverse water leisure space based on clear and clean seas and the recent cruise industry show that the sea itself can be utilized as a resource for tourism. In particular, large cruise ships are generating tremendous wealth and value by sailing through not only the Mediterranean Sea and Europe but also the Pacific Ocean and the Atlantic Ocean.
Furthermore, in the western coast of Korea, there are mudflats of world-class scale. Given the small area of the country, mudflats are useful for constructing seawalls and developing coastline landfills for further utilization. However, in terms of preservation and development of the environment, conflicting views can arise. Therefore, efforts need to be made for sustainable development of the sea for future generation by rationally taking advantage of the infinite possibilities that the sea provides.
※ The texts were written based on the outcome of “development of marine territory educational and promotional data” project pursued by the Korea Maritime Foundation in 2013.